Die Protestation von Gerhard Leibholz gegen die Ernennung von Carl Bilfinger zum Gründungsdirektor des MPIL
Am 27. Juni 1949, nur wenige Wochen nach Verkündung des Grundgesetzes am 23. Mai desselben Jahres, meldete sich der Jurist und frühere Göttinger Professor Gerhard Leibholz (1901‑1982) brieflich beim Präsidenten der Max‑Planck‑Gesellschaft (MPG), Otto Hahn. [1] Im Vorjahr war die noch junge Nachfolgeorganisation der Kaiser‑Wilhelm‑Gesellschaft gegründet worden, der Leibholz von 1926 bis 1929 als Mitarbeiter des Kaiser‑Wilhelm‑Instituts (KWI) für ausländisches öffentliches Recht und Völkerrecht in Berlin angehört hatte. Bereits in jungen Jahren hatte Leibholz eine erfolgreiche akademische Karriere durchlaufen – seit 1929 als Professor an der Universität Greifswald und seit 1931 als Lehrstuhlinhaber an der Universität Göttingen. Die Verfolgung von Leibholz aufgrund seiner jüdischen Herkunft ließ die Laufbahn des protestantisch getauften Sohns einer Berliner Unternehmerfamilie nach Beginn der nationalsozialistischen Diktatur jedoch bald enden. Im Jahr 1935 wurde Leibholz im Alter von 34 Jahren in den Ruhestand und ab 1938 mit seiner jungen Familie in die Emigration gezwungen.
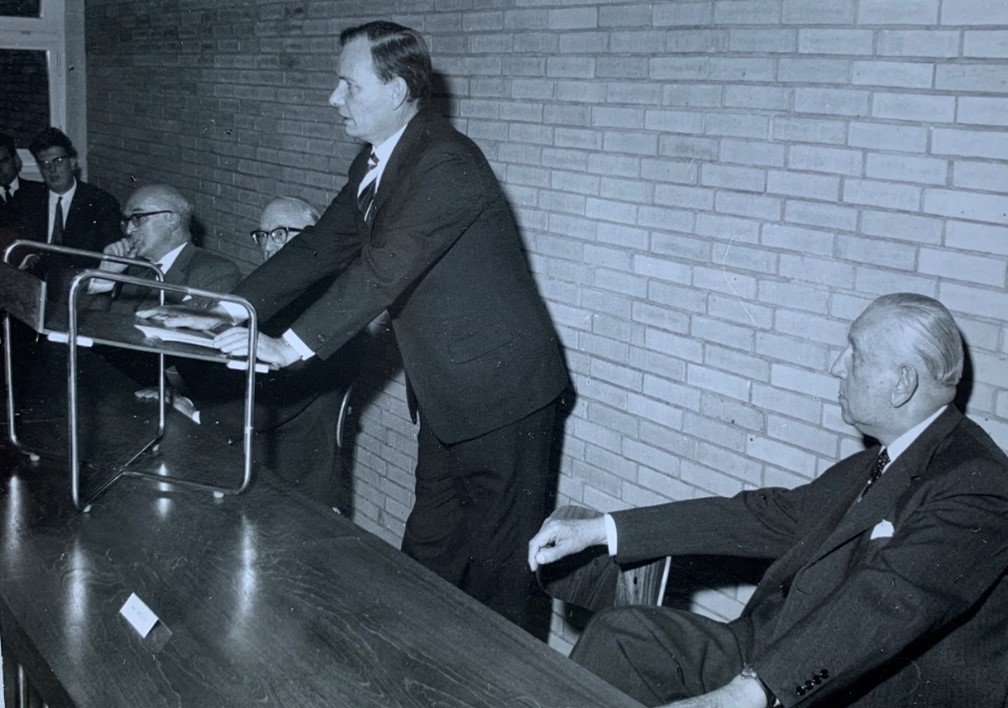
Der Gründungsdirektor Carl Bilfinger (1879-1958)

Carl Bilfinger, Mitte der 1950er [2]
Völlig anders hingegen verlief der Lebenslauf des Juristen Carl Bilfinger (1879‑1958): Dem mittlerweile siebzigjährigen, erst Hallenser, später Heidelberger und schließlich von 1943 bis 1945 Berliner Ordinarius für Öffentliches Recht und Völkerrecht sowie Direktor des KWI für ausländisches öffentliches Recht und Völkerrecht als Nachfolger seines Cousins Viktor Bruns gelang 1949 ein überraschender Neuanfang. Im sowjetischen Machtbereich hatte Bilfinger 1945 als Nationalsozialist bald nach der deutschen Niederlage seine Ämter und Funktionen in Berlin verloren. Ohnedies war er während seiner Berliner Tätigkeit privat in Heidelberg wohnen geblieben. Somit lebte Bilfinger seit 1945 in der US‑amerikanischen Besatzungszone und konnte sich 1948 als „Mitläufer“ erfolgreich entnazifizieren lassen. Im Jahr 1949, als neuerlich berufener Professor der Heidelberger Universität sowie Direktor des dort gegründeten Max‑Planck‑Instituts für ausländisches öffentliches Recht und Völkerrecht (MPIL) stand Bilfinger mithin am Beginn einer zweiten Karriere an seinem (süd-)westdeutschen Wohnort.
Seine Berufung zum Gründungsdirektor des Heidelberger Instituts war aufgrund seiner politischen Vergangenheit keineswegs sicher vorherbestimmt gewesen. Der Jurist und Historiker Felix Lange hat die Entnazifizierung des früheren NSDAP‑Mitglieds in einem Aufsatz und seinem Buch “Praxisorientierung und Gemeinschaftskonzeption” detailliert nachgezeichnet.[3]
Nach dem Ende der NS-Diktatur hatte Bilfinger selbst es keineswegs angestrebt, seinen beruflichen Weg unter den neuen Vorzeichen fortzusetzen. Die grundlegend veränderten Bedingungen schienen dies ohnedies auszuschließen. Als aber doch die Wahl auf ihn als Gründungsdirektor des Heidelberger Völkerrechtsinstituts fiel, verteidigte Bilfinger das frisch gewonnene Amt hartnäckig, frei von jeglicher kritischen Selbstreflexion seiner Rolle während der vorhergegangenen NS‑Diktatur, deren Gefolgsmann er gewesen war.
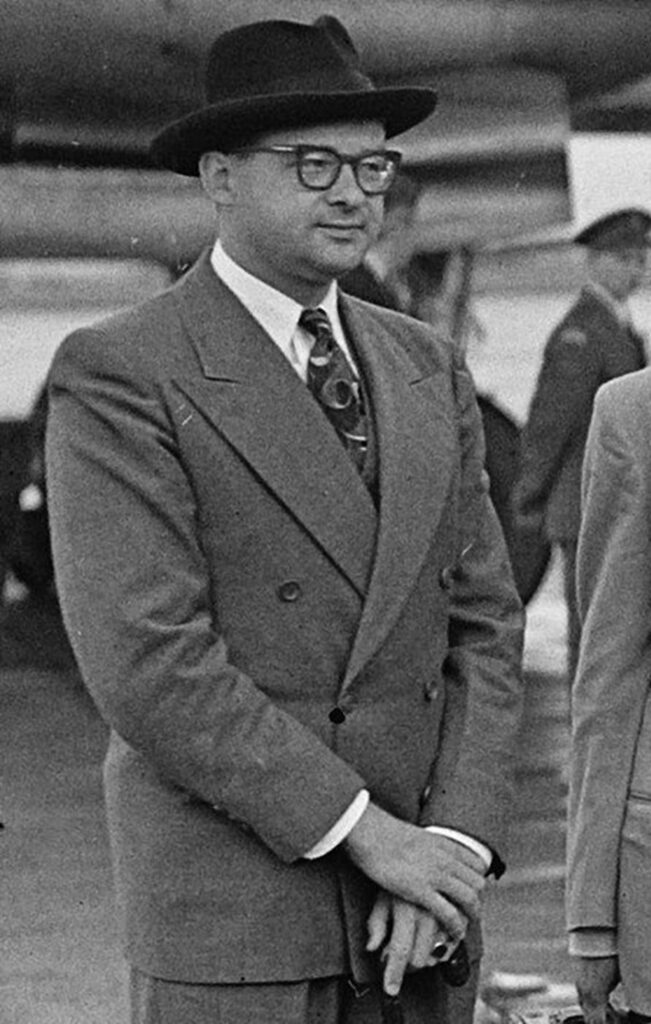
Die Protestnote von Gerhard Leibholz im Jahr 1949

Bundesverfassungsrichter Gerhard Leibholz, 1966 [4]
Als Otto Hahn die knappe briefliche Protestnote von Gerhard Leibholz gegen Bilfingers Ernennung vom 27. Juni 1949 erreichte, war die Entscheidung für Bilfinger bereits unumkehrbar. Dennoch war das Schreiben brisant. Leibholz und Hahn schienen sich bereits zuvor über die Angelegenheit ausgetauscht zu haben. Hahn antwortete Leibholz bereits drei Tage später. Das Präsidium der MPG verfolgte offenkundig das Ziel, sich einerseits loyal gegenüber der eigenen Einrichtung und dem neuberufenen Direktor Bilfinger zu verhalten, andererseits die bereits verbindlich getroffene Entscheidung möglichst überzeugend für den in Deutschland und Großbritannien bestens vernetzten, renommierten Rechtswissenschaftler Leibholz zu begründen; dies nicht zuletzt vor dem Hintergrund von dessen Verfolgungsschicksal und dem seiner Familie als Opfer der NS‑Diktatur. Ein Schwager von Gerhard Leibholz war der Theologe und Widerstandskämpfer Dietrich Bonhoeffer.
Für Leibholz war die Bestellung Bilfingers als neuem Direktor schlicht der Skandal, den diese Berufung tatsächlich darstellte, und der nicht nur Leibholz überrascht hatte. Leibholz selbst stand kurz vor der Wiederaufnahme seiner akademischen Karriere in Deutschland und schaute aus seiner besonderen Perspektive auf die Entwicklungen. In seinen Briefen brachte er seine Verständnislosigkeit, Bestürztheit und Betroffenheit, vor allem aber seine Besorgnis um die Zukunft deutlich zum Ausdruck. Er fühle sich verpflichtet zu sagen, fasste er am 27. Juni 1949 sein Anliegen zusammen,
“dass gerade innerhalb meines Fachbereiches in der Max-Planck-Gesellschaft in der jüngsten Zeit Besetzungen vorgekommen sind, die mich – offen gestanden – sehr betroffen haben […]. Ich denke hier vor allem an Herrn Bilfinger, der vom Braunen Haus in der Zeit, in der der Nationalsozialismus seine Orgien feierte, mit der Leitung des Instituts für ausl[ändisches] öffentl[iches] Recht betraut wurde und der m.W. auch nicht einmal von den deutschen Universitäten reaktiviert wurde. Nach der Zusammensetzung des Senats zu urteilen, an dessen politischer und sachlicher Qualifikation nach Ihren Ausführungen nicht zu zweifeln ist, muss dieser nicht im Besitz zureichender Informationen gewesen sein. Ein Institut wie das des aus[ländischen] öff[entlichen] Rechts und Völkerrechts, an dem ich früher vor 1933 selbst einmal einige Jahre gearbeitet habe und das heute in der Lage wäre, beim Neuaufbau eine wichtige Brücke zum Ausland zu bilden, hätte m.E. als Leiter einen politisch nicht so vorbelasteten Kollegen erhalten müssen, der darüber hinaus – auch zugleich im Ausland – einen gewissen Namen hätte besitzen müssen.”[5]
In seiner Antwort bereits am 30. Juni 1949 verwies Otto Hahn darauf, “dass Professor [Viktor] Bruns selbst Herrn Professor Bilfinger als seinen Nachfolger gewünscht hat. Der Wissenschaftliche Rat der Kaiser Wilhelm-Gesellschaft hat dann später ordnungsgemäß und ohne jede Beeinflussung von politischen Stellen Herrn Professor Bilfinger das Amt des Direktors übertragen.” So sei nach damaliger Auffassung “der beste Wissenschaftler auf dem Fachgebiet” ernannt worden. Mit Blick auf die jüngste Entwicklung schrieb der um Rechtfertigung bemühte Hahn: “In gleicher Weise ist auch die Wiederernennung von Herrn Bilfinger durch ein Gremium erfolgt, dem keine früheren Nationalsozialisten oder der Partei verbundene Persönlichkeiten angehören. Diese Wahl ist in unserem Senat, dem zahlreiche Gegner des nationalsozialistischen Regimes angehören, ausdrücklich gebilligt worden.” Politisch beschwichtigend führte er aus: “Dass Herr Professor Bilfinger Parteimitglied gewesen ist, ist mir bekannt und auch von diesem niemals bestritten worden. Ich glaube aber, dass man daraus noch nicht schliessen kann, dass seine wissenschaftliche Qualifikation dadurch beeinträchtigt wird.”[6]
Leibholz antwortete daraufhin am 3. Juli 1949, dass er Bilfinger nicht seine Parteimitgliedschaft verarge,
„aber die Tatsache, dass er für viele Jahre mit innerer Verve und Überzeugung sich freiwillig dem Nationalsozialismus (als Freund des berüchtigten Staatsrats C[arl] Schmitt) zur Verfügung gestellt und für die Erreichung seiner Ziele eingesetzt hat, ist m.E. allerdings in der Tat geeignet, in einer Zeit, die eine neue Ära einleiten soll, ihn nicht mit der Leitung eines so wichtigen Institutes zu betrauen – ganz abgesehen davon, dass […] der beste Wissenschaftler auf dem Fachgebiet aus dem Jahre 1943 aus offenbaren Gründen nicht identisch mit dem wirklich besten Wissenschaftler aus dem Jahre 1946 seq. ist.”[7]
Hier liege ein offensichtlich “schweres Missverständnis” vor, so Leibholz, insofern der persönliche (Nachfolge-)Wunsch von Bruns zur früheren Ernennung Bilfingers überhaupt maßgeblich beigetragen haben sollte. Der Vorschlag von Bruns sei, so Leibholz, “doch nur aus den damaligen Zeitumständen zu erklären, die nur eine Wahl zwischen einem relativ gemäßigten und einem radikalen Nationalsozialisten” erlaubt habe. Leibholz führte hierzu aus: “So unterliegt es für mich auch nicht dem geringsten Zweifel, dass Herr Bruns[,] wenn dieser nach 1945 berufen gewesen wäre, Namen für das Institut vorzuschlagen, er ganz andere Namen genannt haben würde, obwohl er mit Herrn Bilfinger durch verwandtschaftliche Beziehungen verbunden war.”[8]
Die Reaktion des Gründungsdirektors Carl Bilfinger
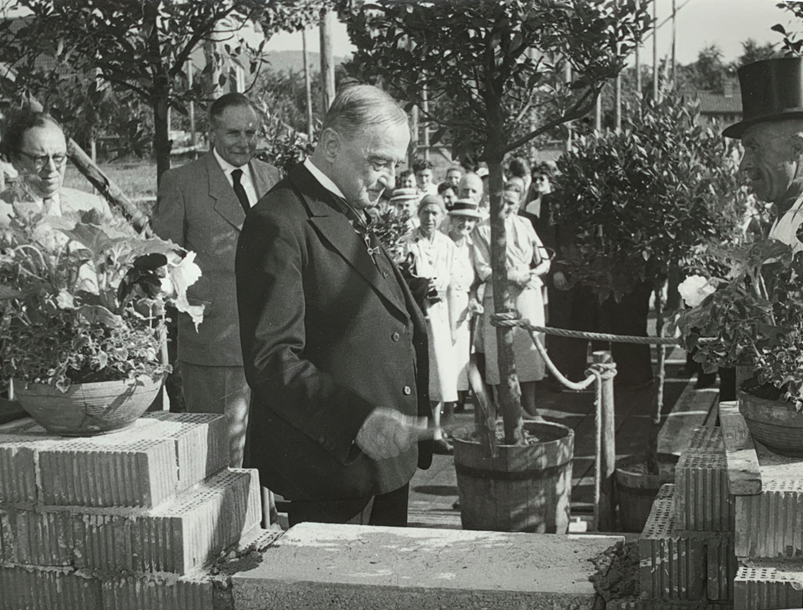

Carl Bilfinger am 24. Juli 1953 bei der Grundsteinlegung des neuen Institutsgebäudes. Sein Richtspruch: „Auf den Fortbestand der Kultur, von der das Recht nur ein Teil ist.“ Am selben Tag war der mit dem großen Bundesverdienstkreuz ausgezeichnet worden.[9]
In dieser Situation suchte Otto Hahn das Gespräch mit Bilfinger selbst, der daraufhin am 10. Juli 1949 an diesen schrieb. Dem Brief legte Bilfinger zu seiner Entlastung verschiedene Materialien in Abschrift bei, die teilweise aus seinem Entnazifizierungsverfahren stammten, unter anderem positive Äußerungen über seine Person von renommierten Fachkollegen wie Eduard Wahl, Heinrich Triepel und Gerhard Anschütz. Besonders Triepel, so Bilfinger, habe maßgeblich dafür gesorgt, dass er 1943 die Nachfolge von Bruns angetreten habe. Ferner bezeichnete Bilfinger die Angaben von Leibholz zu akademischen “Reaktivierungen” im Nachkriegsdeutschland als “irreführend” und ging in einem längeren Abschnitt ausführlich auf seine Kontakte und sein Renommee in der internationalen Gemeinschaft der juristischen Fachkollegen ein. Über sein Verhältnis zu Carl Schmitt schrieb er[10]:
“Auch bemerke ich, dass der im zweiten Brief des Herrn L. erwähnte Staatsrat Carl Schmitt mir allerdings wissenschaftlich und persönlich mehrere Jahre nahe stand, dann aber seit 1934 diese Beziehungen wegen seiner damaligen und folgenden politischen Stellungnahme gegen mich bis auf ein Minimum eingeschränkt waren, was jeder Kenner der Verhältnisse weiss”.[11]
In einem parallel verfassten “persönlichen Brief” vom 11. Juli 1949 an den Generaldirektor der Max-Planck-Gesellschaft Ernst Telschow, den Bilfinger offensichtlich als Gleichgesinnten betrachtete, legte er weniger Zurückhaltung an den Tag. Wütend schrieb Bilfinger: “An und für sich verdient die z.T. etwas kindliche, im ganzen oberflächliche und schlecht informierte Kritik des L. an meiner Person vielleicht keine weitere Antwort.” Dennoch sah er sich aber zu einer persönlichen Stellungnahme berufen. Bilfinger fühlte sich nach erfolgreicher Entnazifizierung zu Unrecht politisch angegriffen und gegenüber dem Präsidium ausgerechnet von Gerhard Leibholz geschmäht, als dessen heimlichen Wohltäter – in Verkehrung des Opfernarrativs – er sich sah. Gegenüber Telschow behauptete Bilfinger, ohne Belege hierfür anzuführen, Leibholz nach Diktaturbeginn im Jahr 1933 geholfen zu haben, sodass er nicht umgehend aus seinem Professorenamt verdrängt worden war. Bilfinger verwies – wiederum ohne Belege – auf die “zahlreichen Fälle, in denen ich, z.T. unter erheblichem Risiko, Juden geholfen habe”. Dies liefere zwar, so Bilfinger, “keinen speziell wissenschaftlichen Befähigungsnachweis für einen Mann, der einige Jahre während der Weimarer Zeit und bis ins erste Halbjahr des NS-Regimes auch dem ´berüchtigten Staatsrat C[arl] Schmitt´ nahestand. Aber, dass nun gerade Leibholz ausgerechnet gegen mich den Spiess vorantragen will, kommt mir komisch vor.”[12]
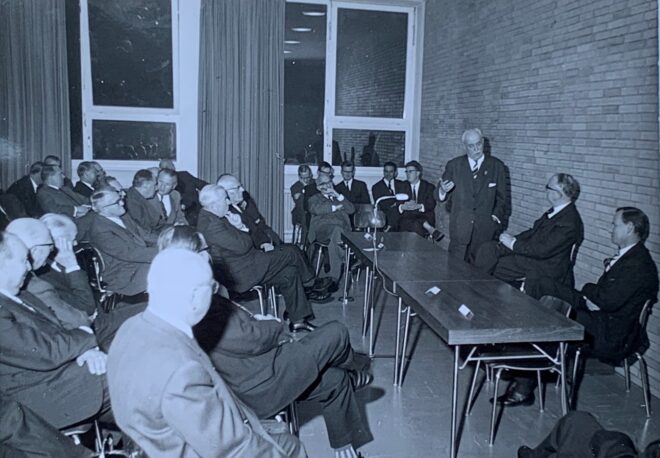
Der Protest bleibt erfolglos und die Dokumente werden ad acta gelegt

Gerhard Leibholz, ab 1962 Kuratoriumsmitglied, nimmt erst nach Bilfingers Tod 1958 wieder am Institutsleben teil. Leibholz (links) mit Jochen Frowein 1970 im Institut[13]
Deutlich später, am 18. August 1949, antwortete Leibholz schließlich mit dem letzten in dieser Korrespondenz von ihm überlieferten Brief. Offensichtlich war zwischenzeitlich sein Schwager Karl‑Friedrich Bonhoeffer, Leiter des Göttinger Max-Planck-Instituts für physikalische Chemie, seitens des Präsidiums in diese Angelegenheit einbezogen worden. Karl‑Friedrich Bonhoeffer hatte Leibholz ein Schreiben Bilfingers zur Einsichtnahme vorgelegt. Es handelte sich vermutlich um das Schreiben von Bilfinger an Hahn vom 11. Juli 1949 nebst Anlagen.
Leibholz blieb jedoch bei seiner bisherigen Auffassung. Gegenüber Otto Hahn brachte er die Angelegenheit auf den Punkt:
“Ich darf noch einmal betonen, dass es sich bei unserer Diskussion nicht um die Frage gehandelt hat, wer 1943 am zweckmäßigsten mit der Leitung des Instituts hätte betraut werden sollen, sondern die zur Diskussion stehende Frage ist, ob jemand, der 1943 als Nationalsozialist mit der Leitung des Instituts betraut wurde und an den Nationalsozialismus bis 1945 geglaubt hat, im Jahre 1949 mit der Leitung des Instituts hätte wieder betraut werden sollen. Alles[,] was ich seit meinem ersten Schreiben in dieser Angelegenheit gehört habe, bestätigt nur, dass es sich bei dieser Entscheidung der Planck-Gesellschaft um eine sachlich-politische Fehlentscheidung handelt. Dies ist im übrigen nicht nur meine persönliche Meinung, sondern die der meisten meiner Fachkollegen.”[14]
Auch wenn sich bei Leibholz wohl spätestens im August 1949 die Erkenntnis durchgesetzt haben dürfte, dass die Entscheidung für Bilfinger nicht mehr rückgängig zu machen war, deutete er am Ende der Auseinandersetzung am 18. August 1949 mit düsterem Unterton hinsichtlich des neu gegründeten Heidelberger Instituts Hahn gegenüber “Folgerungen schwerwiegender, allgemeinerer Art”[15] an, falls an der Personalie Bilfinger festgehalten werden sollte.
Dieser letzte Brief Leibholz´ wurde Bilfinger, so lässt es sich aufgrund der Quellenlage rekonstruieren, zugänglich gemacht. In einem Gespräch kurz vor Verfassen eines neuerlichen Schreibens Bilfingers an Telschow am 19. September 1949 hatte ihn Telschow gefragt, so Bilfinger, “ob es tunlich erscheine, Herrn Leibholz zu einer mündlichen Rücksprache mit dem Herrn Präsidenten [Otto Hahn] einzuladen”[16]. Bilfinger, der offenkundig in dieser Angelegenheit nichts mehr zu befürchten hatte und entsprechend selbstbewusst‑herablassend auftrat, antwortete Telschow nunmehr mit Blick auf ein solches Gespräch, dass es ihm persönlich nicht sicher erscheine, ob der wenig einsichtige und in dieser Angelegenheit nur stark eingeschränkt einsichtsfähige Leibholz “sich gütlich dahin belehren lässt, dass sein Standpunkt irrig und dass ein Eingehen auf seine Anregung nicht möglich” sei. Jedoch sei es auch nicht von vornherein auszuschließen, dass Leibholz im Verlauf eines solchen Gesprächs “nicht doch nachdenklich wird und sich noch einmal gründlich überlegt, ob seine Démarche hinreichend schlüssig begründet und real gedacht ist. Es wäre möglich, dass Herr L. sich durch die Tatsache seines Empfangs und seiner Anhörung durch den Herrn Präsidenten etwas beruhigen könnte.” Es sei somit erwägenswert, Leibholz zu einer Unterhaltung mit dem Präsidenten einzuladen, so Bilfinger, “damit alles geschehen ist, um ihm zu zeigen, dass man seine Vorstellungen angehört hat mit dem Bemühen, ihn und seine Gefühle zu verstehen und ihn nunmehr auch mündlich über den diesseitigen Standpunkt kurz zu informieren”.[17]
Als einige Jahre später eine mögliche Berufung von Gerhard Leibholz ans Heidelberger Institut im Raume stand, reagierte Bilfinger noch aggressiver. Unter Verweis auf die ältere Korrespondenz spitzte er seine Position brieflich am 12. Januar 1952 mit dem Hinweis darauf zu, dass er “das Vertrauen, unter den heutigen Verhältnissen oder in Zukunft mit Leibholz erspriesslich zusammenzuarbeiten, nicht aufbringen [könne]. Daher muss ich Ihnen schon jetzt erklären, dass ich der eventuellen Berufung des Herrn Leibholz mit aller Entschiedenheit widerspreche, und zwar auch für alle weitere Zukunft vor einer solchen Berufung warne.”[18]
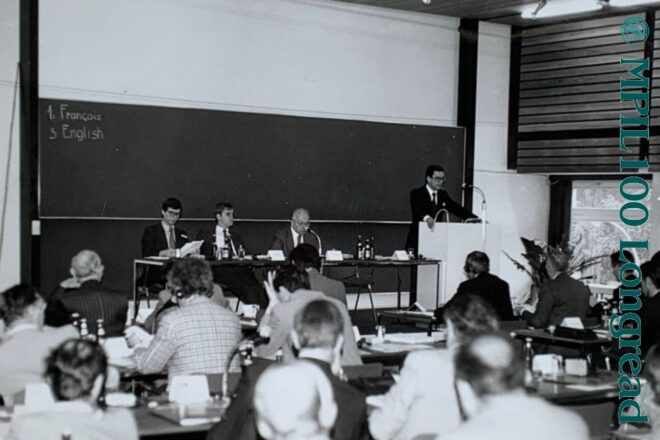
Fazit
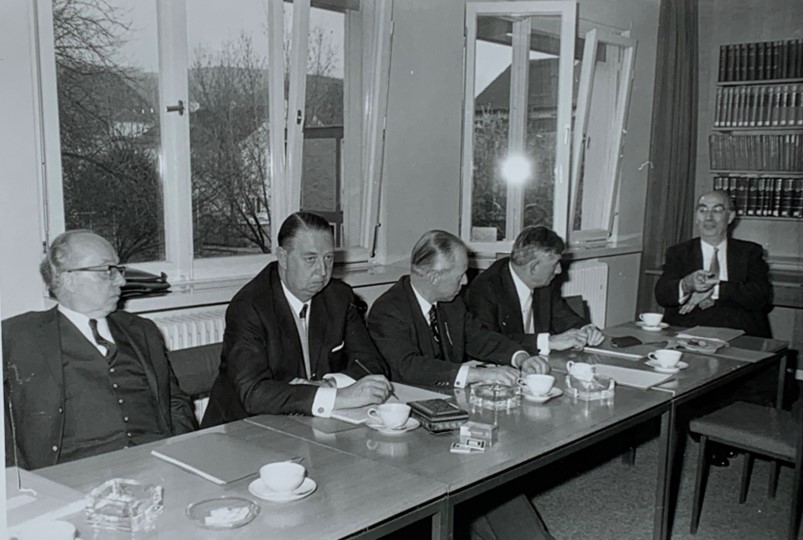

Gerhard Leibholz (rechts) bei der Kuratoriumssitzung am 24. April 1970, mit Helmut Strebel, Günter Jaenicke, Clemens von Velsen und Fritz Münch (von links nach rechts)[19]
Es lässt sich nicht mit letzter Sicherheit feststellen, ob Leibholz unter Verkennung der realen Gegebenheiten, vielleicht in Überschätzung seines persönlichen Ansehens und seiner Möglichkeiten zur Einflussnahme in dieser Angelegenheit, tatsächlich eine Revision der fraglichen Personalentscheidung für Carl Bilfinger für möglich gehalten hat. Oder ob es sich hier, wie es Leibholz wohl schon selbst erkannte, um einen Akt seines persönlichen, im Grunde ohnmächtigen Protests gegen diese personelle Fehlentscheidung handelte. Es war jedoch Leibholz´ Bestreben, wenn schon nicht öffentlich und in direkter Konfrontation, jedoch seinen Einspruch gegen diese Ernennung zumindest unmissverständlich deutlich schriftlich niedergelegt zu haben und in den Akten der MPG für spätere Zeiten aufbewahrt zu finden.
Bilfinger, trotz aller Verärgerung über Leibholz, konnte sich von vornherein sicher sein, dass die für ihn unerfreuliche Angelegenheit – bei entsprechend diskreter Behandlung – bald im Sande verlaufen würde. Dieses Interesse teilte er, wenn auch teilweise anders motiviert, mit dem Präsidium der MPG. Besonders erhellend sind in diesem Zusammenhang die Briefe von Bilfinger an Telschow, in denen erkennbar wird, wie Bilfinger und Telschow tatsächlich dachten. Antisemitische Klischees vom ‚jüdischen Emigranten‘ im ‚Feindstaat‘ Großbritannien, dem in seinem (Rache-)‘Eifer‘ gegen Deutschland – geladen mit Ressentiments gegenüber dem früheren nationalsozialistischen Kriegsgegner – jedwede realistische Einsichtsfähigkeit abgesprochen werden müsse, scheinen deutlich durch. Es ist bezeichnend und vor dem Hintergrund der eigenen Verstrickung in die NS‑Diktatur kaum überraschend, dass für das Leid der NS‑Opfer keine Worte der Anteilnahme oder der kritischen Selbstreflexion, gar der Reue, gefunden werden. Im Kern halten Bilfinger wie Telschow unverändert an ihren früheren Ansichten aus der NS‑Zeit fest, die sie sich jedoch nicht offen zu artikulieren trauen. Bilfinger stilisiert sich gegenüber dem Präsidium sogar – fast zynisch – in Umkehrung der tatsächlichen Verhältnisse zum unschuldigen Opfer eines niederträchtigen Angriffs auf seine Person von außen durch den deutlich jüngeren, ihm angeblich zur Dankbarkeit verpflichteten, jüdischen Emigranten aus Großbritannien und findet zumindest bei Telschow damit offenbar Gehör. Die heikle Angelegenheit sollte aus dieser Sicht möglichst schnell und geräuschlos aus der Welt geschaffen werden. Leibholz war in dieser Situation klug beraten, unter den damals herrschenden Bedingungen die Angelegenheit nicht weiter öffentlich zu skandalisieren. Mit hoher Wahrscheinlichkeit hätte jede andere Vorgehensweise damals ihr Ziel verfehlt oder womöglich gar die gegenteilige Wirkung provoziert.
Am 18. August 1949 schrieb Leibholz in seinem letzten bekannten Brief in diesem Kontext hierzu seinen Standpunkt in dieser Angelegenheit zusammenfassend:
“Ich fühle mich frei von allen Ressentiments, obwohl wir [Leibholz´ Ehefrau Sabine Leibholz-Bonhoeffer und Gerhard Leibholz selbst] 5 Geschwister unter den Nazis auf die grausamste Weise verloren haben, – auch, wie ich ausdrücklich betonen möchte, gegenüber Herrn Bilfinger. Aber es gibt gewisse Dinge, die einfach eine sachlich politische Unmöglichkeit sind. Wenn auch die meisten Wohlgesinnten schweigend und achselzuckend heute solche Dinge hinnehmen, so lege ich meinerseits Wert darauf, ´on record´ niederzulegen, dass ich gegen die Entscheidung der Planckgesellschaft protestiert habe.”[20]
Damit galt die Angelegenheit offiziell als erledigt und der ´Vorgang Leibholz´, der in Wahrheit ein ´Vorgang Bilfinger´ war, wurde im Wortsinn zu den Akten der MPG gelegt.
[1] Die folgende Literatur wurde vor allem für das Verfassen dieses Blogbeitrags herangezogen: Felix Lange, Carl Bilfingers Entnazifizierung und die Entscheidung für Heidelberg. Die Gründungsgeschichte des völkerrechtlichen Max-Planck-Instituts nach dem Zweiten Weltkrieg, ZaöRV 74 (2014), 697-731; Felix Lange, Praxisorientierung und Gemeinschaftskonzeption. Hermann Mosler als Wegbereiter der westdeutschen Völkerrechtswissenschaft nach 1945, Beiträge zum ausländischen öffentlichen Recht und Völkerrecht, Bd. 262, Berlin: Springer 2017; Werner Heun, Leben und Werk verfolgter Juristen – Gerhard Leibholz (1901-1982), in: Eva Schumann (Hrsg.), Kontinuitäten und Zäsuren. Rechtswissenschaft und Justiz im ´Dritten Reich´ und in der Nachkriegszeit, Göttingen: Wallstein 2008, 301-326. Sabine Leibholz-Bonhoeffer, Vergangen, erlebt, überwunden: Schicksale der Familie Bonhoeffer, 2. Aufl., Gütersloh: Gütersloher Verlagshaus Gerd Mohn, 1977.
[2] Foto: MPG Archiv.
[3] Felix Lange, Carl Bilfingers Entnazifizierung und die Entscheidung für Heidelberg. Die Gründungsgeschichte des völkerrechtlichen Max-Planck-Instituts nach dem Zweiten Weltkrieg, ZaöRV 74 (2014), 697-731; Felix Lange, Praxisorientierung und Gemeinschaftskonzeption. Hermann Mosler als Wegbereiter der westdeutschen Völkerrechtswissenschaft nach 1945, Beiträge zum ausländischen öffentlichen Recht und Völkerrecht, Bd. 262, Berlin: Springer 2017.
[4] Foto: BArch, B 145 Bild-F023765-0002 / Engelbert Reinecke.
[5] Schreiben von Gerhard Leibholz an Otto Hahn, datiert 27. Juni 1949, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, Nr. 4473, Bl. 586.
[6] Schreiben von Otto Hahn an Gerhard Leibholz, datiert 30.Juni 1949, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, Nr. 4473, Bl. 587.
[7] Schreiben von Gerhard Leibholz an Otto Hahn, datiert 3.Juli 1949, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, Nr. 4473, Bl. 588.
[8] Schreiben von Gerhard Leibholz an Otto Hahn, datiert 3.Juli 1949 (siehe Fn. 6).
[9] Foto: MPIL.
[10] Über das Verhältnis von Carl Bilfinger und Carl Schmitt, siehe Reinhard Mehring, Vom Berliner Schloss zur Heidelberger „Zweigstelle“. Carl Bilfingers politische Biographie und seine strategischen Entscheidungen von 1944, MPIL100, 9. Februar 2024.
[11] Schreiben von Carl Bilfinger an Otto Hahn, datiert 10. Juli 1949, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, Nr. 4473, Bl. 589.
[12] Schreiben von Carl Bilfinger an Ernst Telschow, datiert 11. Juli 1949, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, Nr. 4473, Bl. 596.
[13] Foto: MPIL.
[14] Schreiben von Gerhard Leibholz an Otto Hahn, datiert 18. August 1949, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, Nr. 4473, Bl. 597.
[15] Schreiben von Gerhard Leibholz an Otto Hahn, datiert 18. August 1949 (siehe Fn. 11).
[16] Schreiben von Carl Bilfinger an Ernst Telschow, datiert 19. September 1949, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, Nr. 4473, Bl. 598.
[17] Schreiben von Carl Bilfinger an Ernst Telschow, datiert 19. September 1949, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, Nr. 4473, Bl. 598.
[18] Schreiben von Carl Bilfinger an [Boris] Rajewsk[y], datiert 12. Januar 1952, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, Nr. 4473, Bl. 603/604.
[19] Foto: MPIL.
[20] Schreiben von Gerhard Leibholz an Otto Hahn, datiert 18. August 1949, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, Nr. 4473, Bl. 597.
|
Suggested Citation:
Johannes Mikuteit, “Einfach eine sachlich politische Unmöglichkeit“. Die Protestation von Gerhard Leibholz gegen die Ernennung von Carl Bilfinger zum Gründungsdirektor des MPIL, MPIL100.de, DOI: 10.17176/20240408-140804-0 |
|
|
Lizenz: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 DEED |
Gerhard Leibholz’s Protest Against the Appointment of Carl Bilfinger as Founding Director of the MPIL
On 27 June 1949, just a few weeks after the promulgation of the Grundgesetz (Basic Law) on 23 May of the same year, the legal scholar and former professor in Göttingen Gerhard Leibholz (1901‑1982) wrote to the President of the Max Planck Society (Max-Planck-Gesellschaft, MPG), Otto Hahn. [1] The MPG had been founded in the previous year as successor organisation to the Kaiser Wilhelm Society, of which Leibholz had been a member from 1926 to 1929 as an employee of the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute (KWI) for Comparative Public Law and International Law in Berlin. At his young age, Leibholz already had a successful academic career – from 1929 he had been a professor at the University of Greifswald and from 1931 at the University of Göttingen. However, the son of a Berlin entrepreneur family, who was baptised as a protestant, was persecuted due to his Jewish origins under the National Socialist dictatorship, which put an end to his career in Germany. Leibholz was forced to retire in 1935 at the age of 34 and had to emigrate with his young family in 1938.
The Founding Director Carl Bilfinger (1879-1958)

Carl Bilfinger, mid 1950s[2]
Legal scholar Carl Bilfinger (1879-1958), on the other hand, had a completely different biography: The now seventy-year-old professor of Public Law and International Law, first in Halle, later in Heidelberg and finally, from 1943 to 1945, in Berlin, who had become director of the KWI for Comparative Public Law and International Law as successor to his cousin Viktor Bruns, made a surprising new start in 1949. In the Soviet occupied zone, Bilfinger, as a National Socialist, had lost his offices and functions in Berlin soon after the German defeat in 1945. However, he had continued to live in Heidelberg during his employment in Berlin. As a result, Bilfinger had been living in the US occupation zone since 1945 and was successfully denazified as a “follower” (“Mitläufer”) in 1948. In 1949, as a reappointed professor at Heidelberg University and director of the newly founded Max Planck Institute for Comparative Public Law and International Law (MPIL) in Heidelberg, the successor to the KWI in Berlin, Bilfinger was thus at the beginning of a second career at his (south)west German place of residence.
Due to his political past, his appointment as founding director of the Heidelberg Institute was by no means predetermined. The lawyer and historian Felix Lange has traced the denazification of the former NSDAP member in detail in an essay and his book “Praxisorientierung und Gemeinschaftskonzeption“.[3]
After the National Socialist dictatorship ended, Bilfinger himself had by no means endeavoured to continue his career under the new circumstances. The fundamentally changed conditions seemed to rule this out anyway. However, when he was chosen as the founding director of the Heidelberg Institute of International Law, Bilfinger stubbornly defended his newly won position, free of any critical self-reflection on his role during the previous Nazi dictatorship, of which he had been a supporter.
Gerhard Leibholz’s Protest Note of 1949

Supreme Court Justice Gerhard Leibholz, 1966[4]
When the President of the MPG, Otto Hahn, received Gerhard Leibholz’s brief protest note against Bilfinger’s appointment of 27 June 1949, the decision for Bilfinger was already irreversible. Nevertheless, the letter was controversial. Leibholz and Hahn appear to have exchanged views on the matter beforehand. Hahn replied to Leibholz just three days later. The Executive Board of the MPG was obviously trying to be loyal to its own institution and the newly appointed director Bilfinger on the one hand, and on the other to justify the already binding decision as convincingly as possible to the renowned and, in Germany as well as Great Britain, very well-connected legal scholar Leibholz. The latter not least against the background of the persecution of Leibholz and his family by the Nazi dictatorship. One of Gerhard Leibholz’s brothers-in-law was theologist and member of the resistance Dietrich Bonhoeffer.
For Leibholz, the appointment of Bilfinger as the new director was simply the scandal that this appointment did in fact represent, and which had taken not only Leibholz by surprise. He himself was about to resume his academic career in Germany and looked at the developments from his own particular perspective. In his letters, he openly expressed his lack of understanding, his dismay and consternation, but above all his concern for the future. On 27 June 1949, he summarized his cause by saying he felt obliged to voice his concern,
“that within my department of the Max Planck Society in particular, there have been recent appointments that have – frankly – affected me very much […]. I am thinking in particular of Mr Bilfinger, who was entrusted with the management of the Institute for Comparative Public Law by the Brown House [The headquarters of the National Socialist German Workers’ Party (NSDAP) in Munich] at a time when National Socialism was celebrating its orgies and who, as far as I know, was not even reactivated by the German universities. Judging by the composition of the Senate, whose political and professional qualifications are not in doubt according to your statements, it must not have been in possession of sufficient information. In my opinion, an institute such as that of Comparative Public Law and International Law, at which I myself once worked for several years before 1933 and which today would be in a position to in the course of rebuilding [Germany] form an important bridge to other countries, should have been given as a director a colleague who is not as politically charged and who furthermore has certain reputation – also abroad.”[5]
In his timely reply of 30 June 1949, Otto Hahn pointed out “that Professor [Viktor] Bruns himself had requested Professor Bilfinger as his successor. The Scientific Council of the Kaiser Wilhelm Society later duly appointed Professor Bilfinger as director without any influence from political authorities.” Thus, in the opinion of the time, “the best scientist in the field” was appointed. Regarding the most recent development, Hahn, attempting to justify the decision, wrote: “In the same way, the reappointment of Mr Bilfinger was made by a committee that did not include any former National Socialists or persons associated with the party. This election was expressly approved by our Senate, which includes numerous opponents of the National Socialist regime.” In a politically placating fashion, he continued: “I am aware that Professor Bilfinger was a party member, and he has never denied it. However, I believe that one cannot conclude from this that his academic qualifications are impaired.”[6]
Leibholz replied on 3 July 1949 that he did not blame Bilfinger for his party membership,
“but the fact that for many years he placed himself with inner verve and conviction at the disposal of National Socialism (as a friend of the notorious State Councillor C[arl] Schmitt) and worked to achieve its goals, is in my opinion, however, sufficient to conclude that, in a time that is supposed to usher in a new era, he should not be entrusted with the management of such an important institute – apart from the fact that […] the best scientist in the field in 1943 is, for obvious reasons, not identical with the actual best scientist in 1946 seq.”.[7]
According to Leibholz, there obviously had to be a “serious misunderstanding”, insofar as Bruns’ personal (succession-)wish had actually contributed significantly to Bilfinger’s earlier appointment. According to Leibholz, Bruns’ proposal could “after all, only be explained by the circumstances of the time, which only allowed a choice between a relatively moderate and a radical National Socialist”. Leibholz concluded: “Accordingly, there is not the slightest doubt in my mind that Mr Bruns, if he had been called upon after 1945 to suggest names for the institute, would have mentioned completely different names, even though he was connected to Mr Bilfinger through family ties.”[8]
The Reaction of Founding Director Carl Bilfinger

Carl Bilfinger on 24 July 1953 at the cornerstone ceremony of the new institute building. His ceremonial dictum translates to: “To the continuation of culture, of which law is only a part.” The same day, he had been awarded with the Federal Cross of Merit (Bundesverdienstkreuz).[9]
In this situation, Otto Hahn sought a dialogue with Bilfinger himself, who then wrote to him on 10 July 1949. To his letter, Bilfinger enclosed copies of various materials in his defence, some of which came from his denazification proceedings, including positive comments about him from renowned colleagues such as Eduard Wahl, Heinrich Triepel and Gerhard Anschütz. According to Bilfinger, Triepel in particular had been instrumental in ensuring that he had succeeded Bruns in 1943. Furthermore, Bilfinger described Leibholz’s statements on academic “reactivations” in post-war Germany as “misleading” and, in a longer section, detailed his contacts and reputation in the international community of legal colleagues. On his relationship with Carl Schmitt, he wrote[10]:
“I also note that I was in close contact academically and personally with the State Councillor Carl Schmitt mentioned in the second letter by Mr Lfor several years, but that since 1934 these relations have been reduced to a minimum because of his political statements against me then and subsequently, as anyone familiar with the circumstances knows.”[11]
In a parallel “personal letter”, dated 11 July 1949, to the Director General of the MPG, Ernst Telschow, whom Bilfinger obviously regarded as like-minded, he showed less restraint. Angrily, he wrote: “In and of itself, the criticism of my person by L, which is in part somewhat childish, overall superficial and ill-informed, perhaps deserves no further response.” Nevertheless, he felt compelled to make a personal statement. After his successful denazification, Bilfinger felt unjustly politically attacked and vilified vis-à-vis the Executive Board, by Gerhard Leibholz of all people, as whose secret benefactor – in a reversal of the victim narrative – he saw himself. In his letter to Telschow, Bilfinger claimed, without providing any evidence, that he had helped Leibholz after the National Socialists’ rise to power in 1933 to not be ousted from his professorship immediately. Bilfinger referred – again, without providing evidence – to the “numerous cases in which I helped Jews, in some cases at a considerable risk “. According to Bilfinger, this did not provide “any special scientific proof of qualification for a man who was also close to the ‘notorious State Councillor C[arl] Schmitt’ for several years during the Weimar period and into the first half of the National Socialist regime. But it seems strange to me that Leibholz of all people should now want to crusade against me.”[12]
The protest Remains Unsuccessful and the Documents are Shelved

Gerhard Leibholz, a member of the curatorium from 1962, became a part of institute life again only after Carl Bilfinger had died in 1958. Leibholz (left) with Jochen Frowein at the institute, 1970.[13]
A considerable time later, on 18 August 1949, Leibholz finally replied with his last letter that has survived from this correspondence. Clearly, in the meantime, his brother-in-law Karl‑Friedrich Bonhoeffer, director of the Max Planck Institute for Physical Chemistry in Göttingen, had been involved in this matter by the Executive Board. Karl‑Friedrich Bonhoeffer had made one of Bilfinger’s letters available to Leibholz. Presumably, it was the letter to Hahn dated 11 July 1949, including attachments.
Leibholz however maintained his previous position. In a letter to Otto Hahn he pointed out:
“I may emphasise once again that our discussion was not about the question of who should most appropriately have been entrusted with the management of the Institute in 1943, but the question under discussion is whether someone who was entrusted with the management of the Institute as a National Socialist in 1943 and who believed in National Socialism until 1945, should have again been entrusted with the management of the Institute in 1949. Everything I have heard since my first letter on this matter only confirms that this decision by the Planck Society was a material-political mistake. Incidentally, this is not just my personal opinion, but that of most of my professional colleagues.”[14]
Even though Leibholz must have realised by August 1949 that the decision in favour of Bilfinger could not be reversed, at the end of the dispute on 18 August 1949, he, in a gloomy undertone, hinted to Hahn with regard to the newly founded Heidelberg Institute about “conclusions of a more serious, more general nature”[15] if the personnel decision regarding Bilfinger were to be upheld.
This last letter from Leibholz was made available to Bilfinger, as can be reconstructed from the sources. In a conversation shortly before Bilfinger wrote another letter to Telschow on 19 September 1949, Telschow had asked him, according to Bilfinger, “whether it would seem expedient to invite Mr Leibholz to a verbal consultation with the President [Otto Hahn]”[16] . Bilfinger, who clearly did not have anything to fear in this matter anymore and acted in a correspondingly confident and condescending manner, now replied to Telschow regarding such a conversation that it did not seem certain to him personally whether Leibholz, who, in his view was hardly perceptive and only capable of a very limited apprehension of this matter, “could be amicably instructed that his point of view is misguided and that it was not possible to accept his suggestion”. However, Bilfinger thought it not entirely inconceivable that Leibniz in the course of such a conversation “might after all become pensive and thoroughly reconsider whether his démarche is sufficiently well-founded and realistically conceived. It is possible that Mr Lcould be somewhat calmed down by the fact that of his reception and hearing by the President.” It was therefore worth considering to invite Leibholz to a meeting with the President, according to Bilfinger, “so that everything has been done to show him that his ideas have been listened to in an effort to understand him and his feelings and to briefly inform him, also in a verbal manner, about this side’s position”.[17]
A few years later, when a possible appointment of Gerhard Leibholz to the Heidelberg Institute came up, Bilfinger reacted even more aggressively. Referring to the earlier correspondence, he made a strong point in a letter of 12 January 1952, stating that he could not “muster up the confidence in being able to work together with Leibholz successfully under the current circumstances or in the future. I must therefore, already at this point, declare to you that I decisively object to the possible appointment of Mr Leibholz and also warn against such an appointment at any point in the future.”[18]
Conclusion

Gerhard Leibholz (right) at the curatorium meeting on 24 April 1970, with Helmut Strebel, Günter Jaenicke, Clemens von Velsen and Fritz Münch (from left to right)[19]
It is not possible to determine with absolute certainty whether Leibholz, failing to judge the situation correctly, perhaps overestimating his personal reputation and his ability to exert influence in this matter, actually thought it possible to revise the decision in favour of the appointment of Carl Bilfinger. Or whether, as Leibholz himself probably recognised, this was an act of his personal, essentially powerless, protest against this misguided personnel decision. However, it was Leibholz’s endeavour to have his objection to this appointment, even if not made publicly and in direct confrontation, at least set down clearly in writing and preserved in the files of the MPG for the future.
Bilfinger, despite his irritation with Leibholz, could be sure from the outset that this unpleasant matter would soon fizzle out – if handled with the appropriate discretion. He shared an interest in that outcome, albeit for partly different reasons, with the MPG’s Executive Board. The letters from Bilfinger to Telschow are particularly illuminating in this context, as they reveal how Bilfinger and Telschow really thought. Shining trough are antisemitic clichés of the ‘Jewish emigrant’ in the ‘enemy state’ of Great Britain, who in his (revenge) ‘zeal’ against Germany – charged with resentment towards the former National Socialist war opponent – is void of any ability to have a realistic view on the situation. It is telling and, against the background of their own involvement in the National Socialist dictatorship, hardly surprising that no words of sympathy for the suffering of the victims of the Third Reich or of critical self-reflection, let alone remorse, are found. In essence, Bilfinger and Telschow continue to cling to their old views from the Third Reich, which they do not dare to articulate openly, however. Towards the Executive Board, Bilfinger even painted himself – almost cynically – in a reversal of the actual situation, as the innocent victim of a vile attack on his person from the outside by the much younger Jewish emigrant from Great Britain, who was supposedly obliged to show him gratitude. At least in Telschow, his narrative apparently found a sympathetic ear. The delicate matter was to be cleared up as quickly and quietly as possible, from this point of view. Under these circumstances and the prevailing conditions at the time, Leibholz was well advised to not further scandalise the matter publicly. Very likely, any other approach would have been unsuccessful or would possibly even provoked the opposite effect.
On 18 August 1949, Leibholz summarised his position on the matter in his last known letter in this context:
“I feel free of all resentment, although we [Leibholz’s wife Sabine Leibholz-Bonhoeffer and Gerhard Leibholz himself] lost 5 siblings under the Nazis in the cruellest way – including, I would like to expressly emphasise, to Mr Bilfinger. But there are certain things that are simply a material political impossibility. Even if most well-meaning people today accept such things silent and shrugging, I, for my part, make a point of putting it on record that I protested against the Planck Society’s decision.” [20]
With that, the matter was thus officially considered closed and the ‘Leibholz affair’, which was in reality a ‘Bilfinger affair’, was, literally, shelved at the MPG.
Translation from the German original: Sarah Gebel
[1] The following literature was consulted primarily for the writing of this blog post: Felix Lange, Carl Bilfingers Entnazifizierung und die Entscheidung für Heidelberg. Die Gründungsgeschichte des völkerrechtlichen Max-Planck-Instituts nach dem Zweiten Weltkrieg, HJIL 74 (2014), 697-731; Felix Lange, Praxisorientierung und Gemeinschaftskonzeption. Hermann Mosler als Wegbereiter der westdeutschen Völkerrechtswissenschaft nach 1945, Contributions on Comparative Public Law and International Law, vol. 262, Berlin: Springer 2017; Werner Heun, Leben und Werk verfolgter Juristen – Gerhard Leibholz (1901-1982), in: Eva Schumann (ed.), Kontinuitäten und Zäsuren. Rechtswissenschaft und Justiz im ´Dritten Reich´ und in der Nachkriegszeit, Göttingen: Wallstein 2008, 301-326. Sabine Leibholz-Bonhoeffer, Vergangen, erlebt, überwunden: Schicksale der Familie Bonhoeffer, 2. ed., Gütersloh: Gütersloher Verlagshaus Gerd Mohn 1977.
[2] Photo: MPG Archive.
[3] Felix Lange, Carl Bilfingers Entnazifizierung und die Entscheidung für Heidelberg. Die Gründungsgeschichte des völkerrechtlichen Max-Planck-Instituts nach dem Zweiten Weltkrieg, HJIL 74 (2014), 697-731; Felix Lange, Praxisorientierung und Gemeinschaftskonzeption. Hermann Mosler als Wegbereiter der westdeutschen Völkerrechtswissenschaft nach 1945, Beiträge zum ausländischen öffentlichen Recht und Völkerrecht, vol. 262, Berlin: Springer 2017.
[4] Photo: BArch, B 145 Bild-F023765-0002 / Engelbert Reinecke.
[5] Letter from Gerhard Leibholz to Otto Hahn, dated 27 June 1949, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, No. 4473, 586, 1. This and all following quotations have been translated by the editor.
[6] Letter from Otto Hahn to Gerhard Leibholz, dated 30 June 1949, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, Nr. 4473, 587, 2.
[7] Letter from Gerhard Leibholz to Otto Hahn, dated 3 July 1949, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, No. 4473, 588, 3.
[8] Letter from Gerhard Leibholz to Otto Hahn, dated 3 July 1949, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, No. 4473, 588, 3.
[9] Photo: MPIL.
[10] On the relationship of Bilfinger and Schmitt, see Reinhard Mehring, Vom Berliner Schloss zur Heidelberger „Zweigstelle“. Carl Bilfingers politische Biographie und seine strategischen Entscheidungen von 1944, MPIL100, 9 Februar 2024.
[11] Letter from Carl Bilfinger to Otto Hahn, dated 10 July 1949, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, No. 4473, 589, 4.
[12] Letter from Carl Bilfinger to Ernst Telschow, dated 11 July 1949, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, No. 4473, 596, 11.
[13] Photo: MPIL.
[14] Letter from Gerhard Leibholz to Otto Hahn, dated 18 August 1949, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, No. 4473, 597, 12.
[15] Letter from Gerhard Leibholz to Otto Hahn, dated 18 August 1949, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, No. 4473, 597, 12.
[16] Letter from Carl Bilfinger to Ernst Telschow, dated 19 September 1949, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, No. 4473, 598, 13.
[17] Letter from Carl Bilfinger to Ernst Telschow, dated 19 September 1949, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, No. 4473, 598, 13.
[18] Letter from Carl Bilfinger to [Boris] Rajewsk[y], dated 12 January 1952, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, No. 4473, 603.
[19] Photo: MPIL.
[20] Letter from Gerhard Leibholz to Otto Hahn, dated 18 August 1949, AMPG II. Abt., Rep. 66, No. 4473, 597, 12.
|
Suggested Citation:
Johannes Mikuteit, „Simply a material political impossibility“: Gerhard Leibholz’s Protest Against the Appointment of Carl Bilfinger as Founding Director of the MPIL, MPIL100.de, DOI: 10.17176/20240408-140943-0 |
|
|
Lizenz: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 DEED |